TECHNICAL TEXTILES
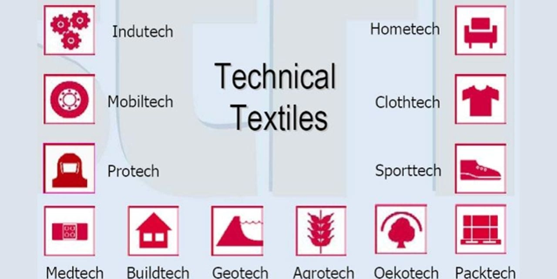
Technical textiles are defined as textile materials and products used primarily for their technical performance and functional properties rather than their aesthetic or decorative characteristics. Other terms used for defining technical textiles include industrial textiles, functional textiles, performance textiles, engineering textiles, invisible textiles and hi-tech textiles. Technical textiles are used individually or as a component/part of another product. Technical textiles are used individually to satisfy specific functions such as fire retardant fabric for uniforms of firemen and coated fabric to be used as awnings. As a component or part of another product, they are used to enhance the strength, performance or other functional properties of that product. Technical textiles have been slowly but steadily gaining ground due to one or more of the reasons such as: functional requirement, health & safety; cost effectiveness; durability; high strength; light weight; versatility; customization; user friendliness; eco friendliness; logistical convenience etc. Unlike conventional textiles used traditionally for clothing or furnishing, technical textiles are used basically on account of their specific physical and functional properties and mostly by other user industries. Depending on the product characteristics, functional requirements and end-use applications the highly diversified range of technical textile are grouped into 11 segments. Segment wise details are as follows:
TECHNICAL TEXTILE SEGMENTS
AGROTECH (AGRO TEXTILES)
BUILDTECH (CONSTRUCTION TEXTILES)
CLOTHTECH (CLOTHING TEXTILES)
GEOTECH (GEO TEXTILES)
HOMETECH (HOME TEXTILES)
INDUTECH (INDUSTRIAL TEXTILES)
MEDITECH (MEDICAL TEXTILES)
MOBILTECH (AUTOMOTIVE TEXTILES)
PACKTECH (PACKAGING TEXTILES)
PROTECH (PROTECTIVE TEXTILES)
SPORTECH (SPORTS TEXTILES)
TECHNICAL TEXTILE TEST FACILITY- AVAILABLE WITH FGT CPS
- FOR FAST SERVICES ADDITIONAL CHARGES WILL BE APPLICABLE:
- 24 HR SERVICE-2 x normal charges
- 48 HR SERVICE-1.5 x normal charges
| Sr. N | TEST PARAMETERS | TEST STANDARD | SAMPLE REQUIRE | TAT/NORMAL SERVICE | FAST SERVICE |
| AIR PERMEABILITY | ISO 9237, IS 11056, ASTM D 737-18, ISO 9073-15 | ||||
| WATER RESISTANCE SPRAY TEST | ISO 4290, lS 390 | ||||
| HYDROSTATIC PRESSURE TEST | ISO 811, AATCC 127, IS 7016 PART-7, ISO 9073-16 | ||||
| WATER IMPACT PENETRATION | AATC C 42 | ||||
| AIR PERMEABILITY | ISO 9237, IS 11056, ASTM D 737-18, I SO 9073-15 | ||||
| WATERPROOF | IS 7016 PART 7 :1986, IS 6803-1972 | ||||
| BUNDESMAN TEST WATER ABSORPTION (%)-PENETRATION OF WATER ML | IS 392- RA2010 | ||||
| MVTR, GM/M DAY | ASTM E-96-95 METHOD B | ||||
| SWEATING GUARD HOT PLATE TEST -THERMAL RESISTANCE (RCT) -WATER VAPOUR RESISTANCE RET | ISO 11092, | ||||
| SURFACE RESISTIVITY | EN ISO 1149-1. | ||||
| ELECTRICAL SURFACE RESISTANCE | EN 1149-5 | ||||
| SURFACE RESISTIVITY | ASTMD 257 | ||||
| STATIC ELECTRICITY | AATCC 134 | ||||
| UV TEST & BREAKING STRENGTH BEFORE AND AFTER UV | ISO 14738-5-200 HRS, | ||||
| UV EXPOSURE | AATCC 186 | ||||
| CO -EFFICIENT OF RETRO REFLECTION -AS RECEIVED | BS EN ISO 20471-2013(OBSERVER ANGLE 12 DEGREE, ENTRANCE ANGLE 5DEGREE), | ||||
| CO -EFFICIENT OF RETRO REFLECTION -AFTER WASHING | BS EN ISO 20471-2013(OBSERVER ANGLE 12 DEGREE, ENTRANCE ANGLE 5DEGREE), | ||||
| CO -EFFICIENT OF RETRO REFLECTION -AFTER DRY CLEANING | BS EN ISO 20471-2013(OBSERVER ANGLE 12 DEGREE, ENTRANCE ANGLE 5DEGREE), | ||||
| CO -EFFICIENT OF RETRO REFLECTION -AFTER CRUMPLE FLEX | BS EN ISO 20471-2013(OBSERVER ANGLE 12 DEGREE, ENTRANCE ANGLE 5DEGREE), | ||||
| TOG VALUE-THERMAL CONDUCTIVITY TEST APPARATUS AT PRESSURE 6.9PA | ISO 5085-1 | ||||
| THERMAL RESISATNCE-TWO PLATE METHOD | BS 4745 | ||||
| TEAR RESISTANCE | ASTM D 5587, ISO 9073-4 | ||||
| ABRASION RESISTANCE | EN 530 METHOD 2 | ||||
| FLEX CRACK RESISTANCE | EN ISO 7854 METHOD B | ||||
| BLOCK RESISTANCE | EN 25978 | ||||
| UPF RATING AND CLASSIFICATION | AATCC 183, ASTM D6603 | ||||
| OMMC | AATCC 195-1 |